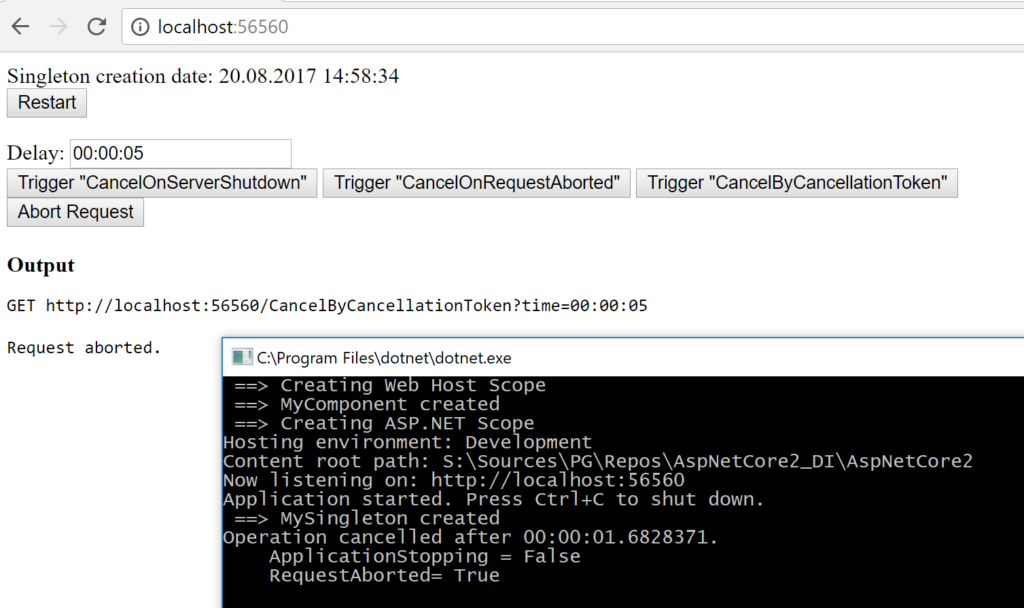
WebHost is about to shut down or that the client is not interested in the response anymore? Especially the latter will occur more often and without proper handling you end up wasting resources for nothing.
- If your component is interested in server shutdown only then you can inject
IApplicationLifetimeand use the propertyApplicationStoppingthat is of typeCancellationToken. Most of asynchronous operations support cancellation tokens so you just have to pass the token to them but be prepare for handling theOperationCanceledExceptionandTaskCanceledException.
public DemoController(IApplicationLifetime appLifetime)
{
_appLifetime = appLifetime;
}
[HttpGet("MyAction")]
public async Task<IActionResult> MyAction()
{
CancellationToken token = _appLifetime.ApplicationStopping;
return await DoSomethingAsync(token);
}
Having a side-free operation like selecting data from database can be cancelled without much effort just pass the CancellationToken to asynchronous methods (like ToListAsync(token)) or check the property CancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested in case you are iterating over some collection or does other synchronous stuff. However, if the operation is critical, the server is shutting down and the component needs a few seconds more to finish then you can delay the shutdown by registering a callback with the CancellationToken.
Use this feature with care, don’t hold up the shutdown indefinitely!
_appLifetime.ApplicationStopping.Register(() =>
{
// server is not going to shutdown
// until the callback is done
});
Note: you can delay the shutdown by overriding the method Dispose of the controller. Using IDisposable-components to finish some stuff works best if you decouple the DI from ASP.NET life cycle like suggested in my previous post because in most cases you want(!) to shut down the WebHost first so that the endpoints are closed and no new requests can come in. Afterwards you can stop your internal processes and dispose of components.
public class DemoController: Controller
{
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
base.Dispose(disposing);
//finish your stuff synchronously
}
}
- Being interested in server shutdown only is more of an edge case. Most of the time it doesn’t matter whether the operation has to stop because of the shutdown or because the client has aborted the HTTP request (e.g. by navigating to another page). In both cases you can use
HttpContext.RequestAbortedwhich is anotherCancellationToken. Although it is called “request-aborted” it is cancelled on shutdown as well because in this case the request is aborted by the server itself not the client.
[HttpGet("MyAction")]
public async Task<IActionResult> MyAction()
{
CancellationToken token = HttpContext.RequestAborted;
return await DoSomethingAsync(token);
}
If the method happens to be an action of an MVC/Web API controller (like in my examples) then you can just specify a new method argument of type CancellationToken to get HttpContext.RequestAborted provided to you.
[HttpGet("MyAction")]
public async Task<IActionResult> MyAction(CancellationToken token)
{
return await DoSomethingAsync(token);
}
Want to try it out? I’ve updated the example from my previous post so that you are able to start and abort HTTP requests or restart the WebHost. The sources are available on Github.